Mencia is to
D.O. Bierzo what the Prieto Picudo and Albarin grapes are to D.O. León. A subregion within Castilla y León primarily dedicated to an historic and signature grape.
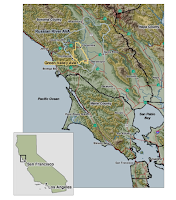
Castilla y León is located in northwestern Spain between Galicia & Portugal and Rioja and is that country's largest wine-producing region -- encompassing 6% of Spain's total production. It is also the 4th largest Spanish grape growing region and home to over 500 wineries. The region contains 14 Designations of Origin (D.O.), four Protected Designations of Origin, and the Vino de la Terra de Castilla y León Protected Geographical Indication (I.G.P.). Castilla y León came into administrative existence in 1983, when the two historical provinces of León and Castilla la Vieja were unified.
According to wine-searcher.com, "Castilla y León's rich cultural history dates back more than two thousand years, as evidenced by its six Unesco world heritage sites. These include the medieval city walls of Avila, the Roman Aqueduct in Segovia, and Atapuerca, an archaeological site rich in Bronze Age and Stone Age artifacts. It may be that wine production in the region pre-dates even the Roman occupation, which began in the 1st Century BC.
In terms of climate, Castilla y León has a remarkably strong continental feel, given how close it comes to the Atlantic Ocean. Hot, dry summers here are followed by sharp, cold winters, when temperatures regularly drop well below freezing. Diurnal temperature shifts are equally pronounced, and play a vital part in the local wine styles. Cool nights refresh the vineyards after long, hot days. The area is completely shielded from the maritime influence of the Bay of Biscay by the Cordillera Cantábrica mountain range. On the other side of these mountains lie the Asturias, Cantabria and Pais Vasco regions. Their cool, fresh climates and fertile hills are in stark contrast to the warm, dry tablelands of Castilla y León.

Wedged between the Cordillera Cantábrica and the Sistema Central mountains, the region occupies a vast plateau about 200km (125 miles) across and between 700 and 1000 meters (2,300ft - 3,300ft) above sea level. Given this location and the low rainfall, soils here are typically thin and poor. They do become richer in minerals and clays, however, near the region's rivers, of which there are many.
D.O. Bierzo lies in the far northwest of Castilla y Leon close to the region's borders with Galicia. The viticultural area consists of two parts: Bierzo Alto (high Bierzo), a mineral-rich and mountainous terrain where terraced vineyards are sewn into the slopes, and Bierzo Bajo (low Bierzo), a wide and verdant plain. Bierzo's proximity to the Atlantic Ocean has a profound effect on its overall climate, with average temperatures during the growing season much cooler than in Castilla y Leon's more inland areas, making it rather mild. Nevertheless, the Cordillera Cantábrica mountain range in the north provides the vineyards with adequate shelter. This ensures that the Mencia grapes achieve optimum ripeness.
Bierzo's soil is different from that found in other parts of Castilla y Leon in that it contains a predominance of slate and granite. This favors the Mencia vines and helps them to produce wines with a distinct mineral character. The wines tend to be lighter in terms of alcohol and more refreshing than those from other parts of Castilla y León.
Mencia is a thick-skinned, violet-blue grape that was once thought to be related to Cabernet Franc. Modern DNA testing has disproved this theory, however, but has uncovered that it is genetically identical to Portugal's Jaen." It's its origin Bierzo or Dão?
"Mencia wines tend to exhibit earthy, vegetal characters with berry nuances and stony minerality. They have a bright complexion with a vivid maroon color, relatively fresh acidity and tannins. The fruit flavors can range from red to black fruits, often with a herbal dimension of mint or thyme. The variety can be challenging in the vineyard, and has a tendency towards low yields, making it a challenging prospect for growers and winemakers. It is susceptible to botrytis and mildew, and can lose its acidity quickly if not harvested promptly. Mencia's high alcohol and moderate acidity provide something of a juggling act at harvest and in the winery. Oak is used sparingly, as it can overwhelm Mencia's rather delicate flavor profile."
At the
Castilla y León Roadshow, I sampled several Mencia wines from two producers who focus almost exclusively on this grape. Elva Garcia Amigo was onsite representing her winery --
Aníbal de Otero (Daughter of Anibal) -- named in honor of her father. Aníbal and his father tended their Mencia vines which are now more than 100 years old. The process is overseen by oenologist José Hidalgo where the grapes are hand harvested in small batches, fermented in stainless steel and aged at various lengths in French oak. In the vineyard they practice sustainable practices where aromatic plants, wild oregano, thyme, and chamomile grow wild as cover crops.
Anibal de Otero Mencía, D.O. Bierzo 2022
Made exclusively with Mencía grapes from bush-ripened vines with an average age of over 90 years. Located near the village of Otero de Toral, on a steep, high altitude of 500-600 meters with clay, sand, slate, and pebbles. The grapes are naturally fermented in stainless steel tanks. The wine is aged three months in used 225-liter French oak barrels, then 8-10 months in stainless steel tanks before bottling, and bottle ageing for at least 6 months. This is a fresh and pleasant Mencia with abundant red fruit and juicy acidity.
Anibal de Otero Villa, D.O. Bierzo 2018
The grapes are from the same 90+ year old vines as the Anibal de Otero Mencía but the best grapes are separated and used for the Villa. Similar fermentation process, but longer aging with six months in used 225-liter French oak barrels and at least 18 months in the bottle. More velvety texture surrounds the red fruit and balanced tannins leading to bright acids.
Anibal de Otero Los Fornos, D.O. Bierzo 2016
The grapes are harvested from very small plots in the exclusive Los Fornos area. The vineyard is south-facing, on a slope overlooking the valley where the Burbia and Cúa rivers meet the Sil where the soils are dominated by limestone and slate. The wine follows a similar fermentation process but the aging is extensive. It involves 18 months in new and used 225-liter French oak barrels then bottle aged for at least 36 months. This a complex and wonderful wine - darker fruit, more approachable tannins, and tasty earthiness.
Cantariña Vinos de Familia is another small winery started by five siblings cultivating 13 Ha of 100 year old family vineyards divided among three different sites in their Villafranca del Bierzo hometown. The first is
Viña de Los Pinos, one of the most iconic and photographed vineyards in Bierzo. It sits by the Camino de la Virgen, a narrow dirt path transited by thousands of Pilgrims each year on their way to Santiago de Compostela. The second and older site is
Valdeobispo and the third and newest site is
Cotelo, where parts had been abandoned for 20 years. Valdeobispo was first planted in 1910 and considered one of the grand crús in Bierzo. The soils are clay and sand with limestone and rolling stones.
Cantariña Villafranca, D.O. Bierzo 2022
This wine is practically 100% Mencia with trace amounts of Palomino, Doña Blanca and Godello in a field blend from the Viña de Los Pinos and Valdeobispo sites. The grapes are naturally fermented in 5000 liter oak vats with partial use of whole cluster. The wine is then aged in oak vats and used 225 and 500 liter French oak barrels. Fresh red fruit characterizes this wine with subtle spice and earthiness.
Cantariña Valdeobispo, D.O. Bierzo 2021
This is 100% Mencia from the the iconic and organic Valdeobispo site. The grapes are fermented in an 50 HL oak vat, whole clustered, the aged 12 months in used 225 and 500 liter French oak casks. This wine has an astonishing vibrant mouthfeel, lively tannins and acidity distributing velvety dark fruit most notably blackberries.
















.png)


























